Unveiling the Cosmos: A Comprehensive Guide to Space Terms and Cosmic Wonders
The universe, with its vastness and mysteries, has captivated human imagination for centuries. As we delve into the realm of space exploration, it becomes essential to familiarize ourselves with the plethora of terms that define this cosmic expanse. From celestial bodies to scientific phenomena, this article aims to unravel the intricacies of space terms, shedding light on the wonders that await our exploration.
- Galaxies
At the heart of the cosmos lie galaxies, colossal systems comprising stars, planets, gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The Milky Way, our home galaxy, is just one among billions in the observable universe.
- Stars
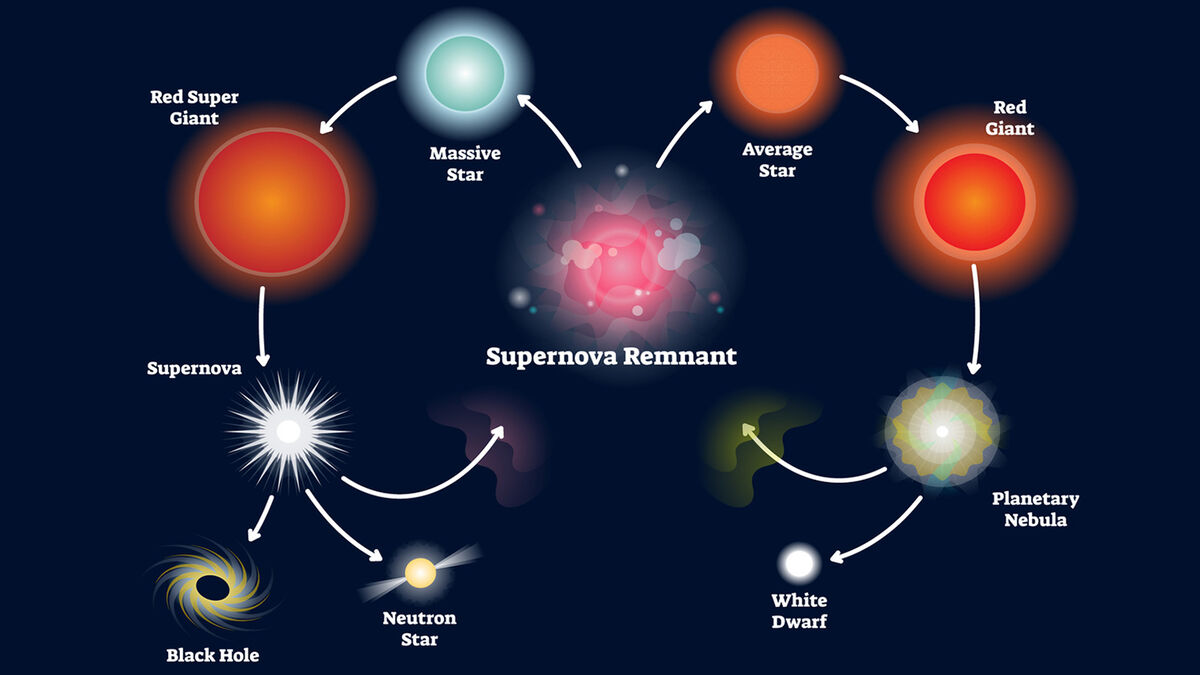
Stars, the celestial luminaries that dot the night sky, are massive balls of gas undergoing nuclear fusion, releasing energy in the form of light and heat. Our sun, a medium-sized star, sustains life on Earth.
- Planets
Orbiting stars, planets are diverse worlds ranging from gas giants like Jupiter to rocky terrains like Earth. Our solar system boasts eight planets, each with its own unique characteristics.
- Asteroids and Comets
Smaller celestial bodies, asteroids, and comets are remnants of the early solar system. Asteroids are rocky and metallic, while comets are icy bodies that develop tails when approaching the sun.
- Nebulae
Nebulae are vast clouds of gas and dust, often serving as stellar nurseries. These stunning formations birth new stars and planetary systems.
- Black Holes
Black holes are regions in space where gravity is so intense that nothing, not even light, can escape. They form when massive stars collapse under their gravity.
- Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Though invisible, dark matter and dark energy make up a significant portion of the universe. Their nature remains elusive, but their presence is inferred through their gravitational effects.
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)
The CMB is the residual radiation from the Big Bang, filling the entire universe. Studying the CMB provides crucial insights into the early moments of the cosmos.
- Quasars
Quasars are incredibly bright and energetic objects powered by supermassive black holes at their centers. They emit intense radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Exoplanets
Beyond our solar system, exoplanets orbit stars in other galaxies. Their discovery expands our understanding of planetary systems and the potential for life beyond Earth.
- Constellations
Constellations are patterns of stars in the night sky, often forming recognizable shapes. Different cultures have assigned mythological stories and significance to these groupings.
- Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that employs the principles of physics to understand celestial phenomena. It explores the nature of stars, galaxies, and the overall structure of the universe.
- Telescopes
Telescopes, both ground-based and space-based, are instrumental in observing distant celestial objects. They collect and amplify light, enabling astronomers to study the universe in detail.
- Space Exploration
Human endeavors to explore space involve sending spacecraft, rovers, and probes to study distant planets, moons, and other celestial bodies. Mars rovers and the Voyager probes are iconic examples.
- Orbit
The path an object takes around another celestial body is called its orbit. Orbits can be elliptical, circular, or hyperbolic, depending on the gravitational forces at play.
- Satellites
Artificial satellites orbit Earth, providing invaluable data for communication, weather monitoring, and scientific research. The International Space Station (ISS) is a prominent example.
- Gravity
Gravity is the force that attracts objects with mass towards each other. It plays a fundamental role in shaping the structure of the universe.
- Light-Year
A light-year is a unit of distance, representing the distance light travels in one year. It is often used to measure vast cosmic distances.
- Supernova
A supernova is a stellar explosion that can outshine entire galaxies for a brief period of time. It disperses heavy elements into space, enriching the cosmos with new materials.
- Astrobiology
Astrobiology explores the potential for life beyond Earth, considering the conditions necessary for life to exist on other planets or moons.
Conclusion
As we unravel the cosmos and push the boundaries of space exploration, understanding these space terms becomes pivotal. Whether you’re an amateur stargazer or a seasoned astronomer, the language of the universe is universal. Each term represents a unique aspect of the cosmic tapestry, inviting us to explore the mysteries that lie beyond our earthly confines. Embracing these concepts is a journey into the unknown, where the wonders of the universe await our discovery.



